Vagrant
Vagrant is an open source provisioning tool from Hashicorp. It uses a concept of “boxes” and is used to provision development environments at scale to a multi cloud environment – where depending on your install environment, you can customise installs for Hyperv, KVM, Virtualbox, VMware, AWS etc
Installing is pretty straightforward. For linux distros, usually a yum or an apt-get will get the installation going.
For a MAC, this is what I had to do:
- Download the binary from Hashicorp
- Installation is GUI based and pretty straightforward
- Post installation, Vagrant can be accessed from the command line


Post installation, you can invoke Vagrant from the command line
Ayans-MacBook-Pro:~ ayan$ vagrant
Usage: vagrant [options] <command> [<args>]
-v, --version Print the version and exit.
-h, --help Print this help.
Common commands:
box manages boxes: installation, removal, etc.
cloud manages everything related to Vagrant Cloud
destroy stops and deletes all traces of the vagrant machine
global-status outputs status Vagrant environments for this user
halt stops the vagrant machine
help shows the help for a subcommand
init initializes a new Vagrant environment by creating a Vagrantfile
login
package packages a running vagrant environment into a box
plugin manages plugins: install, uninstall, update, etc.
port displays information about guest port mappings
powershell connects to machine via powershell remoting
provision provisions the vagrant machine
push deploys code in this environment to a configured destination
rdp connects to machine via RDP
reload restarts vagrant machine, loads new Vagrantfile configuration
resume resume a suspended vagrant machine
snapshot manages snapshots: saving, restoring, etc.
ssh connects to machine via SSH
ssh-config outputs OpenSSH valid configuration to connect to the machine
status outputs status of the vagrant machine
suspend suspends the machine
up starts and provisions the vagrant environment
upload upload to machine via communicator
validate validates the Vagrantfile
version prints current and latest Vagrant version
winrm executes commands on a machine via WinRM
winrm-config outputs WinRM configuration to connect to the machine
For help on any individual command run `vagrant COMMAND -h`
Additional subcommands are available, but are either more advanced
or not commonly used. To see all subcommands, run the command
`vagrant list-commands`.
Provisioning is as easy as single command
Ayans-MacBook-Pro:~ ayan$ vagrant init hashicorp/precise64
A `Vagrantfile` has been placed in this directory. You are now
ready to `vagrant up` your first virtual environment! Please read
the comments in the Vagrantfile as well as documentation on
`vagrantup.com` for more information on using Vagrant.
Bringing up the environment is a matter of running “vagrant up“
Ayans-MacBook-Pro:~ ayan$ vagrant up
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Box 'hashicorp/precise64' could not be found. Attempting to find and install...
default: Box Provider: virtualbox
default: Box Version: >= 0
==> default: Loading metadata for box 'hashicorp/precise64'
default: URL: https://vagrantcloud.com/hashicorp/precise64
==> default: Adding box 'hashicorp/precise64' (v1.1.0) for provider: virtualbox
default: Downloading: https://vagrantcloud.com/hashicorp/boxes/precise64/versions/1.1.0/providers/virtualbox.box
default: Download redirected to host: vagrantcloud-files-production.s3.amazonaws.com
==> default: Successfully added box 'hashicorp/precise64' (v1.1.0) for 'virtualbox'!
==> default: Importing base box 'hashicorp/precise64'...
==> default: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> default: Checking if box 'hashicorp/precise64' is up to date...
==> default: Setting the name of the VM: ayan_default_1546749336149_84625
Vagrant is currently configured to create VirtualBox synced folders with
the `SharedFoldersEnableSymlinksCreate` option enabled. If the Vagrant
guest is not trusted, you may want to disable this option. For more
information on this option, please refer to the VirtualBox manual:
https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch04.html#sharedfolders
This option can be disabled globally with an environment variable:
VAGRANT_DISABLE_VBOXSYMLINKCREATE=1
or on a per folder basis within the Vagrantfile:
config.vm.synced_folder '/host/path', '/guest/path', SharedFoldersEnableSymlinksCreate: false
==> default: Vagrant has detected a configuration issue which exposes a
==> default: vulnerability with the installed version of VirtualBox. The
==> default: current guest is configured to use an E1000 NIC type for a
==> default: network adapter which is vulnerable in this version of VirtualBox.
==> default: Ensure the guest is trusted to use this configuration or update
==> default: the NIC type using one of the methods below:
==> default:
==> default: https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/virtualbox/configuration.html#default-nic-type
==> default: https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/virtualbox/networking.html#virtualbox-nic-type
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
default: Adapter 1: nat
==> default: Forwarding ports...
default: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
==> default: Booting VM...
==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
default: SSH username: vagrant
default: SSH auth method: private key
default:
default: Vagrant insecure key detected. Vagrant will automatically replace
default: this with a newly generated keypair for better security.
default:
default: Inserting generated public key within guest...
default: Removing insecure key from the guest if it's present...
default: Key inserted! Disconnecting and reconnecting using new SSH key...
==> default: Machine booted and ready!
==> default: Checking for guest additions in VM...
default: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
default: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
default: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
default: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
default: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
default: your host and reload your VM.
default:
default: Guest Additions Version: 4.2.0
default: VirtualBox Version: 5.2
==> default: Mounting shared folders...
default: /vagrant => /Users/ayan
Ayans-MacBook-Pro:~ ayan$
Now my MAC has Virtualbox running – it auto detects the Virtualbox, configures the environment and powers on the VM
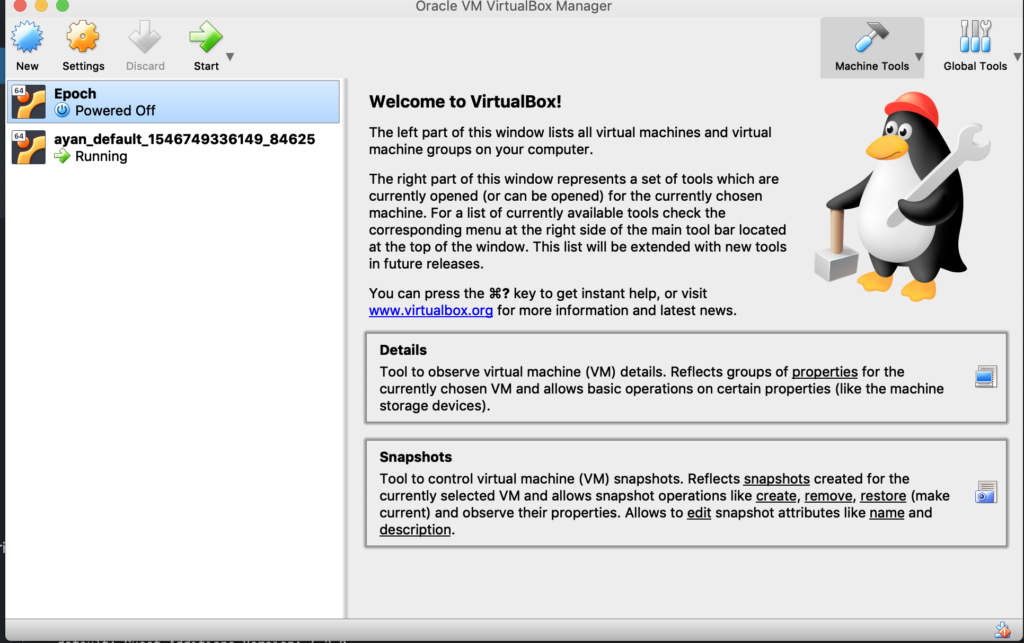
The ayan_default_XXX is the environment that is created. Powering off or deleting can be done using the appropriate vagrant command. For this one, I am deleting (destroying) the VM
yans-MacBook-Pro:~ ayan$ vagrant destroy
default: Are you sure you want to destroy the 'default' VM? [y/N] y
==> default: Forcing shutdown of VM...
==> default: Destroying VM and associated drives...
Stay tuned for more